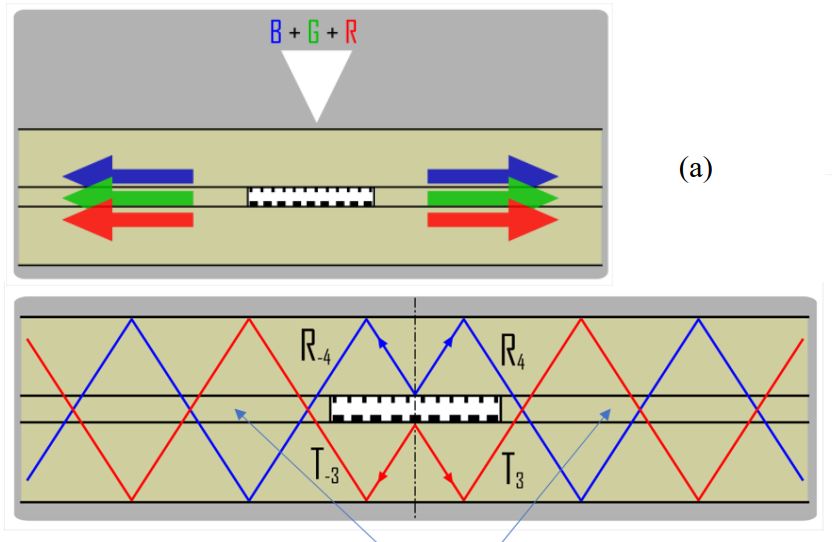
In this work we propose several full-color metagrating solutions for single waveguide-based
Augmented and Virtual Reality near-eye display systems. The presented solutions are based on a combination of
reflective and/or transmissive diffraction gratings inside or outside a waveguide. The proposed in-coupler
designs have high diffraction efficiency across a wide angular range. Applying our new grating combination
solution, we can provide good gathering of diffracted rays for the different colors. We demonstrate that by using
a dual-mode symmetrical in-coupling system and angular pupil tiling, we can extend the overall horizontal FoV
for three RGB colors. The new characteristics of the full single waveguide system including Eye Pupil Expander
and out-coupling components compatible with the proposed in-coupling solutions are discussed. We show that a
new nonsymmetrical design of metagratings can be used to change its diffraction properties improving the
diffraction efficiency and diffraction uniformity of the optical components.
“Metagrating solutions for full color single-plate waveguide combiner” Oksana Shramkova * , Valter Drazic, Guillaume Bourcin, Bobin Varghese, Laurent Blondé, and Valérie Allié , Metamaterials for Novel Wave Phenomena in Microwaves, Optics, and Mechanics. 2022.
Skip to PDF content
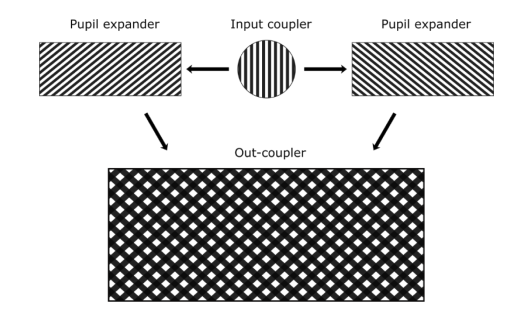
Waveguide based optical combiners for augmented reality (AR) glasses are integrating several surface relief gratings (SRG) whose pitch sizes can be as small as 200 nm for the blue wavelength. All SRG components exploit the first diffraction order to couple in and out or to deviate the light. We present SRG using higher diffraction orders featuring over-wavelength pitch sizes. Our gratings use the edge wave (EW) diffraction phenomenon to steer light in the
preferred far field direction.
“Over-wavelength pitch sized diffraction gratings for augmented reality applications .“, Drazic, Valter; Shramkova, Oksana; Varghese, Bobin; Blondé, Laurent; De La Perrière, Vincent Brac; Schiffler, Jesse; Twardowski, Patrice; Lecler, Sylvain; Walter, Benjamin; Mairiaux, Estelle; Bavedila, Fuanki; Faucher, Marc; Allié, Valérie. 2022 Optics Express 30(2) 1293-1303
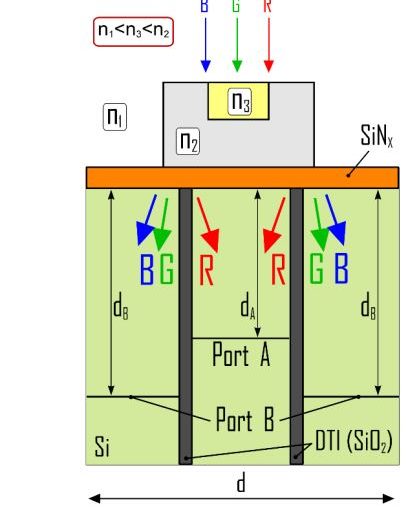
We propose a new type of color splitter, which guides a selected bandwidth of incident light to-wards the proper photosensitive area of the image sensor by exploiting the nanojet (NJ) beam phenomenon. Such splitting can be performed as an alternative to filtering out part of the re-ceived light on each color subpixel. We propose to split the incoming light thanks to a new type of NJ-based near-field focusing double-material element with an insert. To suppress crosstalk, we use a Deep-Trench-Isolation (DTI) structure. We demonstrate that the use of a dielectric insert block allows for reduction in the size of the color splitting element. By changing the position of the DTI, the functionality of separating blue, green and red light can be improved.
“Optical efficiency enhancement of nanojet-based dielectric double-material color splitters for image sensor applications .“, Oksana Shramkova *, Valter Drazic, Bobin Varghese, Laurent Blondé and Valerie Allié , Nanomaterials 10th November 2021.
Skip to PDF content
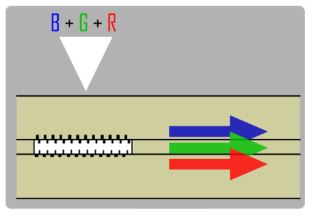
In this work we propose a new type of metagrating solution based on a combination of two diffraction gratings embedded inside the waveguide. We demonstrate that the proposed design has high intensity across a wide angular range and can be used as single waveguide full color combiner for AR application.
“Full color waveguide combiner with embedded metagrating.“, O. Shramkova, L. Blondé, V. Drazic, B. Varghese, V. Allié, 15th International Congress on Artificial Materials for Novel Wave Phenomena – Metamaterial 2021, New-York, USA.
Skip to PDF content
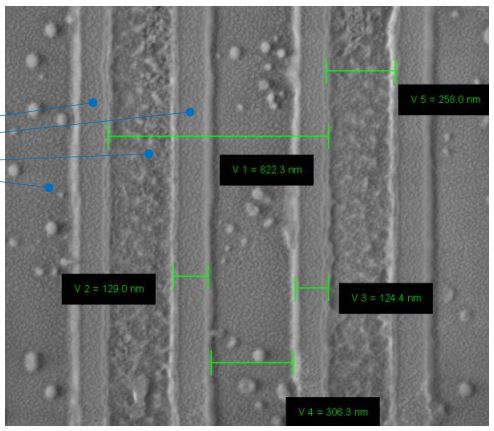

In this work we propose a new type of symmetrical surface relief diffractive grating for waveguide-based Augmented Reality near-eye display system with a wide Field of View (FoV). We demonstrate that by using a dual-mode symmetrical in-coupling system and angular pupil tiling, we can extend the overall horizontal FoV. Our grating coupler is optimized for the second diffraction orders. The proposed concept is validated numerically via full-wave electromagnetic analysis of a 1D diffraction grating. Measurements of the diffraction efficiency of the micro-fabricated prototype are compared with the results of the numerical simulation
“High-uniformity dielectric U-shaped surface relief grating coupler for AR headsets.“, O. Shramkova, V. Drazic, B. Varghese, L. Blondé, V. Brac De La Perriere, V. Allié, SPIE Nanoscience and Engineering, 2021, San Diego, USA.
Skip to PDF content
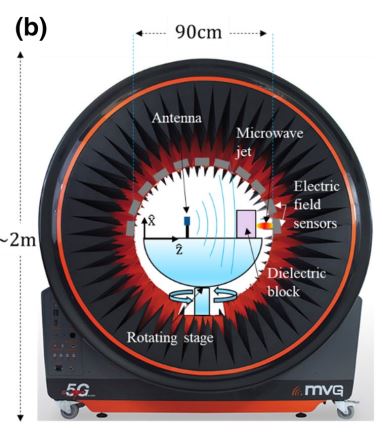
In this paper, we report the experimental and numerical investigation of plane wave diffraction by an all-dielectric dual-material cuboid. Edge diffraction by a cuboid leads to the generation of a narrow, high intensity beam in the near-field region called a photonic jet. We examine the dependence of the jet behavior and orientation on the materials and dimensions of constitutive parts in the microwave frequency domain. The possibility to shift and deviate the resultant microwave jet in the near-field region of such a structure depending on the size of constitutive parts is demonstrated numerically. Experimentally, we observe a shift in the spatial position of the jet. The experimental asymmetric electric field profile observed in the far-field region is attributed to the input of multiple edge waves generated by the dual-material cuboid. The presented results may be scaled at different frequency bands such as optical frequencies for designing nanostructures enabling the focusing and deviation functionality and creation of new optical devices which would satisfy the needs of emerging nanophotonic applications.
“Experimental observation of asymmetrical microwave jets and far-field distribution generated by a dual-material system“, B. Varghese1, , O. Shramkova1, P. Minard2, L. Blondé1, V. Drazic1, V. Allié1, Scientific reports, june 2021.
Skip to PDF content
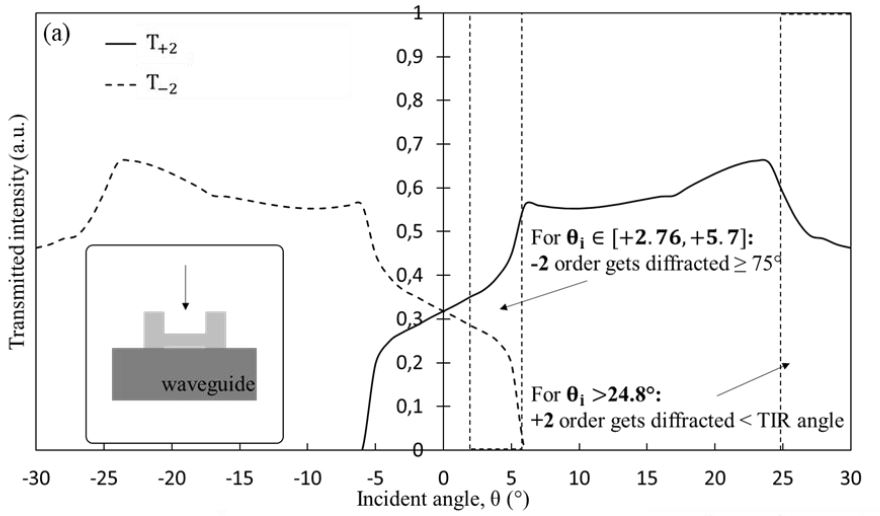
There are multiple challenges to realize waveguide-based Surface Relief Gratings (SRG) for combiners in Augmented Reality (AR) applications: fabricability, efficiency and diffraction uniformity are among the most important ones. Interdigital develops SRG using Edge Waves (EW) to design highly efficient gratings with a high angular robustness. An EW is generated by a diffraction phenomenon appearing at the interface between two dielectric media and its direction of propagation is controlled by the index ratio between the two media and the direction of the incident plane wave. Combining different edges together, we optimize the elementary geometry, i.e., the building block of an SRG, to diffract into the direction defined by the grating equation, optimizing the power transfer of the incident light into the direction of interest. Our approach enables symmetrical structures with low aspect-ratio, optimized for coupling very efficiently into the first or second order modes, the latter leads to over-wavelength pitch sizes. Moreover, our SRG is designed to angularly tile the exit pupil of the light engine without losses, making our structures adapted to any sort of light engines. Based on our unique design concept, we present in-couplers using two waveguides with a field of view of 130 degrees and RGB operation, and a one waveguide system with 90 degrees of field of view and RGB operation, both with a wafer having also an index of refraction of about 1.7. We believe this will pave the way to new DOE combiners for future AR glasses.
“High-uniformity, high-performance double material dielectric diffractive metagratings.“, Valter Drazic , Oksana Shramkova, Bobin Varghese, Laurent Blondé, Valérie Allié, 1SPIE Photonics West, Augmented, Virtual and Mixed Reality (AR, VR, MR) II, March 2021, San Francisco, USA.
Skip to PDF content
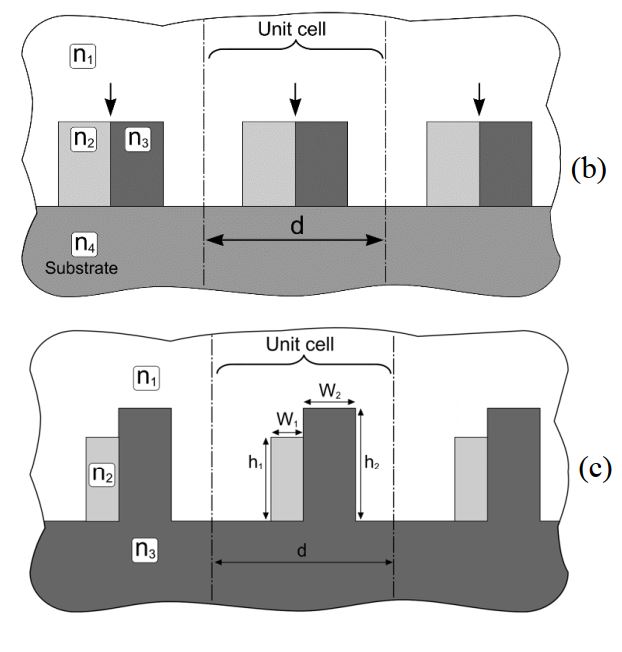
In this work we propose a solution for the creation of a nanojet focusing component based on a combination of two dielectric materials capable of managing the position of the focused beam in the near zone. We demonstrate that the double-material design of the elements of metagratings can be used to change its diffraction properties improving the diffraction efficiency and diffraction uniformity.
“High-uniformity, high-performance double material dielectric diffractive metagratings.“, O. Shramkova, V. Drazic, L. Blondé, B. Varghese, V. Allié, 14th International Congress on Artificial Materials for Novel Wave Phenomena – Metamaterial 2020, New-York, USA.
Skip to PDF content
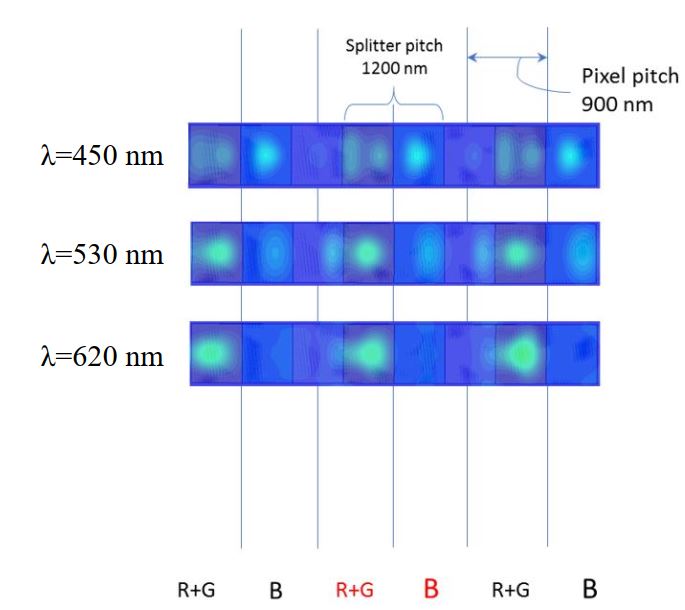
In this work we have developed new types of color splitters, which separate spectrally and spatially the light that falls on image sensors by exploiting the nanojet (NJ) beam phenomenon. The proposed method relies on light diffraction on the edges of constitutive parts of the studied multi-material elements embedded in a host medium with lower refractive index. Diffraction of light on the edge of a dielectric microstructure forms a tilted focused beam whose deviation angle depends on the refractive index ratio between the materials of the elements creating this edge. The characteristics of the generated NJ beams are also controlled by the geometry of multi-material elements (size and base angle of the edge) and the angle of wave incidence. Combination of two or more dielectric materials with different refractive indexes leads to the creation of multiple NJs with different angles of deviation, length and intensity. In the case of normally incident plane wave, the generated NJ beams originating from different edges of the constitutive parts of a multi-material microstructure, recombine and contribute to the formation of NJ beam deflection away from the normal direction in the near zone. The possibility to split color-bands of the incident light by combining two or more dielectric materials in such a way that the generated NJ beams create a spectrally dependent NJ beam deflection is discussed. We demonstrate that the proposed topologies of multi-material microlenses help to reduce the size of the color splitting element and optical crosstalk through the active Si layer. We show that the color splitting functionality of the proposed exists for inclined incident light as well. Applying these color splitters to actual image sensors allows to improve the optical efficiency by splitting the incoming light between the image sensor pixels, instead of filtering out part of the received light.
“Nanojet-based dielectric multi-material color splitters for image sensor applications.“, Oksana Shramkova*, Valter Drazic, Laurent Blondé, Bobin Varghese, Valérie Allié, SPIE Photonics Europe, April 2020, Strasbourg, France (Online).
Skip to PDF content
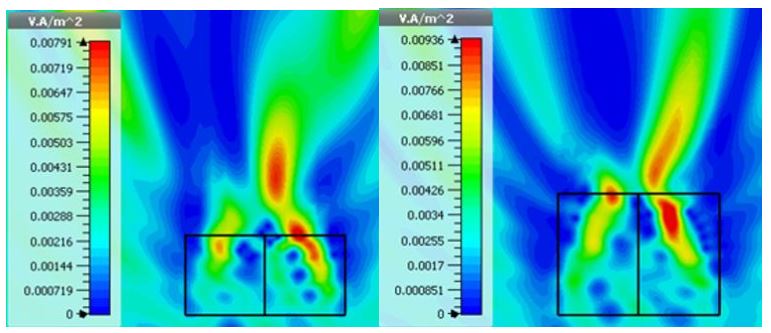
In this paper we study high-intensity nanojet (NJ) beams generated at the output of dielectric multi-material elements. The proposed method for generating condensed optical NJ beams relies on the complex electromagnetic phenomenon associated with the light diffraction on the edges of constitutive parts of the studied system embedded in a host medium with lower refractive index. The possibility of NJ shift and deviation in the near zone of such a microstructure illuminated by a plane wave is demonstrated via a double-material microstructure. We examine the dependence of NJ beam behavior and orientation on the materials and dimensions of the constitutive parts.
“Photonic nanojet generated by dielectric multi-material microstructures.“, Oksana Shramkova*, Laurent Blondé, Valter Drazic, Bobin Varghese, Valérie Allié , META July 2019, Lisbon, Portugal.
Skip to PDF content









